- Website security certificates
- How does an SSL certificate work?
- SSL certificate for websites
- How to get an SSL certificate
- Best free SSL certificate
- Next steps
- Hosting with Tiiny.host
- FAQ - How to Get a Free SSL Certificate for Your Website
HTTPS
Knowing your website is secure can help you sleep at night. Attacks are increasing even on small sites. Relieve some of the stress of worrying. Learn what it takes to protect your website investment.
One crucial step in your website security is installing an SSL certificate. You can get one for free, and they’re easy to install.
Not sure what an SSL certificate is or why you need one?
Read on.
Website security certificates
A website security certificate is a digital file containing your website’s security and identity profile. Certificates are issued by a Certificate Authority (CA). The CA is a trusted authority that ensures your site is not fake and is encrypted using the Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) protocol.
SSL is an industry-standard encryption protocol that ensures hackers cannot breach the connection between your server and your visitor’s browser. This keeps your site and the visitor’s information safe and secure.
All websites should have an SSL certificate, not only those that sell something. For instance, private login information—any data visitors send to or receive from your website—must be encrypted for privacy.
How does an SSL certificate work?
Earlier, I said an SSL certificate contains your website’s security and identity profile. But it’s actually more than that. It also contains code that encrypts your internet connections.
When a browser connects to your website, an SSL “handshake” is enacted by the certificate server. During this handshake, the SSL, web server, and browser are recognized, and a secure connection is made. The connection is invisible and instantaneous.
The connection is not made if the handshake fails—the communication is terminated. This keeps your privacy intact.
SSL certificate for websites
Many certificate authorities issue SSL certificates. All SSL certificates have several features in common.
- Encryption: Data is encrypted so that only the intended recipient can decipher it
- Fragmentation: Data is sent in several fragments rather than one large chunk
- Confidentiality: Guaranteed through encryption
- Integrity: Ensured through encryption
- Authentication: Provided through digital authenticity certificates, which are difficult to falsify
- Safety and convenience: SSL creates a secure connection between a client machine and a server
- Prevention of attacks: SSL helps prevent eavesdropping, impersonation, data theft, identity theft, and phishing attacks
- Authenticity: SSL guarantees that a website represents itself truthfully
SSL certificate types
In addition to these features, SSL certificates are of three types. These types concern the validation efforts made to identify the certificate holder.
Extended Validation (EV SSL): Requires the most validation effort, including validating the holder’s phone, address, and legal validity. Used by business and e-commerce sites.
Organization Validated (OV SSL): Validates a business’s legal identity and ensures that the business is real and is who they say they are. Deters phishing attacks. Designed for mid-level business use.
Domain Validated (DV SSL): Single-step validation consisting of an email to the WHOIS record. This simple verification proves that someone is the owner of a specific domain. Used by millions of smaller websites. Often issued free of charge.
How to get an SSL certificate
It’s simple to get an SSL certificate. There are several ways to do it.
Free SSL with hosting
The easiest and cheapest way to get SSL certification is by using a web host that automatically provides a free SSL certificate when you use their hosting services. Tiiny.host is such a service.
Free one-click installs
Hosting services, such as Dreamhost, offer one-click SSL certificate installation on any domain you host with them. These services usually also offer more sophisticated, paid certificates too.
Paid SSL certificates
Various hosting services and vendors offer a variety of paid, highly secure SSL certificates.
For example, the Comodo SSL Store offers a range of certificates—DV, OV, EV—with a wide range of prices based on features such as money-back guarantees and warranties.
Prices on the Comodo SSL store range from under $10 a year for a DV to over $2,000 per year for EV validation.
Best free SSL certificate
The most popular free SSL certificate is issued by the CA Let’s Encrypt.
Let’s Encrypt is a non-profit, automated DV certificate CA. Dozens of industry leaders sponsor it, such as AWS, Cisco, and IBM. Let’s Encrypt servers over 300 million websites.
Usually, you get a Let’s Encrypt certificate through your web hosting service. There is also a self-hosted method if you have your own servers.
Next steps
If you’re looking to host a website with a free, automatically-installed SSL certificate, try Tiiny.host. Or, if you have any questions about SSL certificates or web hosting in general, Tiiny.host’s awesome customer service team is available to help you free of charge. Visit Tiiny.host/help to reach out by chat or email.
Hosting with Tiiny.host
Tiiny.host, our service, is the simplest way to host your website, PDF, file, or demo.
Three steps is all it takes, and your project is live on the web!
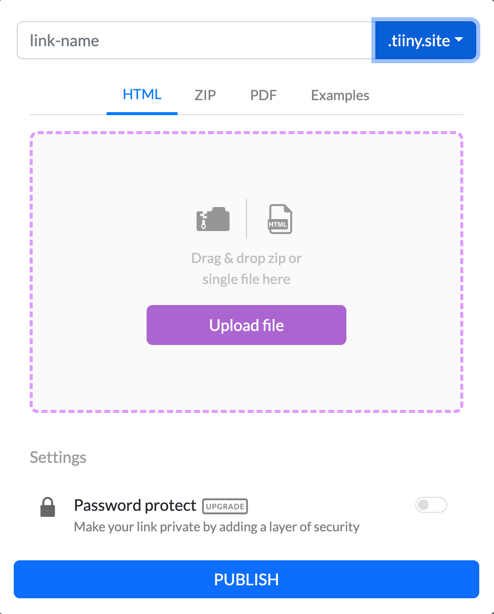
Sign in for free, then follow these three steps:
- Provide a link-name as the name of your project.
- Drag and drop your zipped project into the Upload File dialog box.
- Click the big, blue PUBLISH button.
That’s it!
Wait a moment, and your project is live on the web.
You can access your new website at https://link-name.tiiny.site. Free!
Please let us know how we can be of further assistance.
Visit Tiiny.host, or Tiiny.host/help.
FAQ - How to Get a Free SSL Certificate for Your Website
What is an SSL certificate, and why do I need one for my website?
SSL is a security technology that encrypts data between websites and browsers. It protects sensitive information like credit card transactions, logins, and data transfers. Google ranks SSL-secured websites higher in search results, but that’s not the main value. Your web visitor’s data—all of it—requires privacy and security. So does yours.
Are there free SSL certificates available, and are they safe to use?
Yes, there are a number of free SSL certificate providers such as Let’s Encrypt, Cloudflare, and SSL.com. These organizations provide standard Domain Validation (DV) SSL certificates that are just as secure as those sold by other vendors. They are trusted by most browsers and work well for websites that require basic encryption.
Is there any downside to using a free SSL certificate?
While free SSL certificates provide the same level of encryption as paid ones, they come with certain limitations. They often only offer Domain Validation (DV), the lowest validation level. For e-commerce sites or those handling sensitive data, a higher level of validation, like Organization Validation (OV) or Extended Validation (EV), may be needed. These paid certificates range widely from under $10 a year for DV to over $1,000 per year for EV-level validation.



