- Implementing Website Security
- Building a Secure Website
- Adopting Website Security Best Practices
- The Role of Backups
- Recommendations
- Next steps
- Contact Tiiny.host
- FAQ—How to Improve Your Website Security
How to Improve Website Security: Best Practices and Essential Steps
Website security dominates the thoughts of most website owners. Or at least it should.
Website security best practices are fundamental to a safe and useful site. Just about everyone knows this, but putting these practices and features into action often gets forgotten or overlooked. Many website owners don’t even realize these best practices exist.
Getting hacked is no fun. This article addresses the basics of website security so you can implement them on your site.
Here we go.
Implementing Website Security
The best way to implement website security is to design it into your site from the beginning.
Secure web design is the first essential step when starting or reworking a web development project.
Building a Secure Website
Privacy Protection Features
Secure websites call for a web design process that keeps security in mind throughout.
Privacy protection features for website components such as consent forms, cookies management systems, online privacy notices, and secure user login pages are crucial. If your web visitors’ information isn’t secure on the website, hackers can gain access to everything from passwords to credit card numbers.
Website Firewalls
A website firewall serves as a gatekeeper, observing all the data entering the server and blocking anything that doesn’t belong, like viruses and malware.
Firewalls are fundamental website security features. They are usually set up and maintained by your web hosting service or by your own developers if self-hosting.
Choosing a firewall depends on factors like complexity, cost, and the level of security needed.
Firewalls for small businesses are less complicated but just as secure as those for medium to large businesses. There are many things to configure in a website firewall, and this configuration generally requires the services of a developer familiar with web hosting.
Adopting Website Security Best Practices
SSL Certificates and Encryption
Acronyms are a big part of understanding web security. Let’s start with SSL and TLS.
Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) is a web protocol that makes the connection between the web server and the browser encrypted and secure. Encryption turns plain text into a digital code that is virtually unbreakable. The code is sent between web devices and browsers, and hackers can’t read what is being sent.
Transport Layer Security (TLS) is the more secure successor to SSL, but nowadays, the acronym “SSL” is commonly used to denote both. You may also see “TLS/SSL” when dealing with encryption, such as when connecting an email client to your email’s host computer.
Getting SSL to work on your website means installing an SSL Certificate on your server.
There are paid solutions for complicated websites like large e-commerce sites. But free SSL certificates are available.
Most good web hosting companies offer pre-installed or one-click-install free SSL certificates, usually by the Let’s Encrypt certificate provider.
RECOMMENDED ARTICLE: How to get a free SSL certificate for your website
Two-Factor Authentication
Two-factor authentication (2FA) is common today. Whenever a website or mobile app has you sign up, they offer to let you use 2FA to log into your account.
2FA requires you to prove your identity using two distinct verification methods—such as a username and password plus a text message sent to your phone. You may have done this several times yourself.
2FA dramatically reduces the chance of an unauthorized person accessing your account.
But there are still more best practices to implement. Website security is not only limited to security measures, but also to learning more about cybersecurity. Resources like the MITRE ATT&CK framework offer accessible information about adversary tactics, techniques, and behavior, allowing you to integrate this knowledge into security tools and develop robust strategies.
The Role of Backups
“Did you back up your work?”
This is a familiar question to most computer users. Well, think how much work goes into building and maintaining a website! You must back them up too.
Website backups can prevent catastrophic business losses if your server suddenly goes down.
All that’s necessary to retrieve your website is to install it again from a backup. Then you’re back in business. Failure to have a backup means your business may not come back online for weeks, months, or perhaps ever.
It’s best to have multiple backups—both on-site and off-site. Online backups make sure your information is not stored only locally. You may lose your backup copy if something happens to your physical server. You’ll be glad you have copies in at least two places. Three is even better, depending on your fail-safe security requirements.
Recommendations
Website security is a large and complicated topic. A great deal of time and effort goes into web security, and much of it requires well-trained personnel.
When shopping for a web hosting service, we recommend you keep web security best practices in mind. Ideally, you can find a hosting service that does all this work for you in advance. All you must worry about is the design of your site. The web host takes care of SSL certificates, firewalls, and all that technical but necessary infrastructure.
Next steps
Our service, Tiiny.host, makes hosting a secure website as simple as possible.
All the servers and storage are fast and secure using industry best practices. SSL certificates for your site are included for free. You needn’t worry about hosting your site with Tiiny.host’s built-in security.
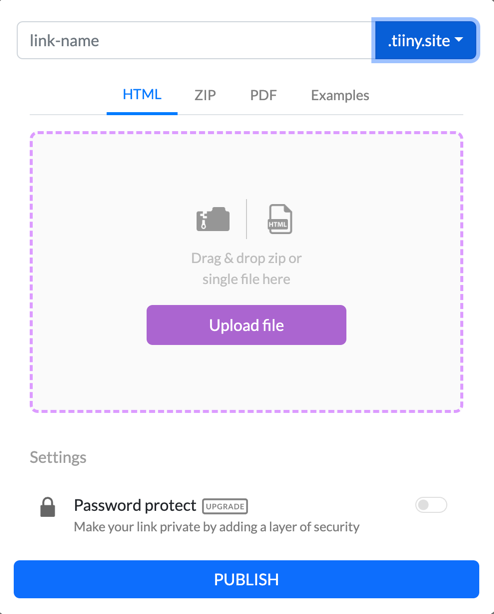
All you must do is log in for free, then take three simple steps:
- Provide a link-name as the name of your website.
- Drag and drop your zipped website to upload it
- Press the big, blue PUBLISH button.
That’s it!
Now wait a few seconds, then….BOOM!
Your website is live on the web.
It really doesn’t get any easier than that.
Contact Tiiny.host
If you have any questions about this article, web hosting, or anything else internet related, visit Tiiny.host/help/. Their awesome customer service is there to help you out.
FAQ—How to Improve Your Website Security
What is an SSL certificate, and why do I need one?
An SSL certificate authenticates a website’s identity and encrypts data to protect sensitive information from being intercepted by hackers. It also improves user trust and may boost SEO ranking.
What is two-factor authentication, and how does it enhance website security?
Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) requires users to verify their identity with two different methods, such as a password and a mobile device. This enhances website security and reduces the risk of unauthorized access.
How can I back up my website, and why is it necessary?
Website backups are important to restore your site to a previous state in case of data loss or a cyberattack. You can manually download or use automated backup solutions from your web host or third-party services to store copies of your content, databases, and related information.



